Database security services
Database Security Service (DBSS) is an intelligent database security service. Based on the machine learning mechanism and big data analytics technologies, it can audit your databases, detect SQL injection attacks, and identify high-risk operations.
1.Functions
Database audit delivers functions such as user behavior detection and audit, multi-dimensional lead analysis, real-time alarms, and reports.
- User Behavior Detection and Audit
- Associates access operations in the application layer with those in the database layer.
- Uses built-in or user-defined privacy data protection rules to mask private data (such as accounts and passwords) in audit logs displayed on the console.
-
Multi-dimensional Lead Analysis
-
Behavior analysis
Supports analysis in multiple dimensions, such as audit duration, statement quantity, risk quantity, risk distribution, session statistics, and SQL distribution.
-
Session analysis
Conducts analysis based on time, user, IP address, and client.
-
Statement analysis
Provides multiple search criteria, such as time, risk severity, user, client IP address, database IP address, operation type, and rule.
-
-
Real-time Alarms for Risky Operations and SQL Injection
-
Risky operation
Defines a risky operation in fine-grained dimensions such as operation type, operation object, and risk severity.
-
SQL injection
Provides an SQL injection library, which facilitates alarm reporting for database exceptions based on the SQL command feature or risk severity.
-
System resource
Reports alarms when the usage of system resources (CPU, memory, and disk) reaches configured threshold.
-
-
Fine-grained Reports for Various Abnormal Behaviors
-
Session behavior
Provides session analysis report of the client and database users.
-
Risky operation
Provides the risk distribution and analysis report.
-
Compliance report
Provides compliance reports that meet data security standards (for example, Sarbanes-Oxley).
-
2.Compared the professional and advanced editions
| Version | Maximum Databases | System Resource | Performance | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professional | 6 | $1500/monthly | ||
| Advanced | 30 | $5000/monthly |
3.Constraints
Database audit is subject to certain constraints. It's support Mysql/Oracle/PostgreSQL/SQL Server/DWS/Greenplum/MongoDB/Hbase etc. You can reference the official page.
Supported Database Types
The following types of databases on HUAWEI CLOUD can be audited in out-of-path mode:
- RDS instances
- Databases built on ECS
- Databases built on BMS
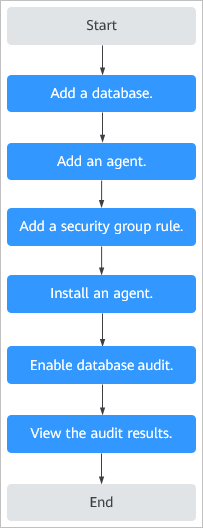
4.Configuration
Procedure for quickly configuring database audit
The deployment support agent and without agent. Without Agent only support cloud-native database. The agent deployment for database audit is as follows:
- For databases built on ECS or BMS, agents must be deployed on the database side.
- For relational databases, agents must be deployed on the application or proxy side.
Auditing a User-built Database on ECS
Auditing a User-built Database on ECS
Auditing an RDS DB instance (with Agents)
Auditing an RDS DB instance with Agents
Auditing an RDS DB Instance (Without Agents)
Auditing an RDS DB Instance Without Agents
5.总结
用英文写真TM费劲,最后这个总结用中文来一个汇总吧。先说下数据库安全检测所能提供的功能:
- SQL注入防护:内置多种SQL注入攻击特征库,精准识别攻击行为并告警通知
- 风险操作检测:数据库慢SQL检测、数据库拖库检测
- 日志异常行为检测:使用机器学习技术,对数据库审计日志进行分析,识别异常行为并告警
为什么需要数据库安全
从两方面看:外部攻击者越权连接数据库进行数据篡改、窃取;内部工作人员违规访问敏感数据。所以从这两天方面来看,使用DBSS可以消除以下问题:
- 非法操作无法溯源
- 事中违规行为无告警
- 缺失独立审计系统
像这里的审计能力,实际上在SQL自身的日志也可以实现,但自身实现存在的一个问题是,没有独立性、数据容易被 修改,没有报表等功能。
数据库审计需要计录什么
其实无论现实世界的审计还是应用系统的审计,一般都可以通过 5w 来概括:
- who(谁): 连接数据库的应用名、源IP
- where(来源):请求数据库的源IP、MAC、应用信息
- when(时间):什么时候请求的,请求的时长多久
- waht(做了什么):查询的表、对象是啥?有没有请求成功?当时的查询对性能是否有影响?返回了多少行、多少列的数据?
- How(怎么干的):SQL语句是什么?传入的参数提什么?
捐赠本站(Donate)

如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))