06 velero backup
Backup and disaster recovery
1. Install the velero software
| [root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# wget https://github.com/vmware-tanzu/velero/releases/download/v1.11.1/velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# tar zxvf velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/LICENSE
velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/examples/minio/00-minio-deployment.yaml
velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/examples/nginx-app/README.md
velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/examples/nginx-app/base.yaml
velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/examples/nginx-app/with-pv.yaml
velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/velero
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# mv velero-v1.11.1-linux-amd64/velero /usr/local/bin/
|
create the AK/SK credentials file
| # vim credentials-velero
[default]
aws_access_key_id = {AK}
aws_secret_access_key = {SK}
|
Currently, the S3 protocol is used in the industry, and HUAWEI CLOUD OBS also supports the S3 protocol. Therefore, set Provider to aws.
| velero install \
--provider aws \
--plugins velero/velero-plugin-for-aws:v1.7.1 \
--bucket veleroback01 \
--secret-file ./credentials-velero \
--use-volume-snapshots=false \
--backup-location-config region=sa-brazil-1,s3ForcePathStyle="true",s3Url=http://obs.sa-brazil-1.myhuaweicloud.com
|
veleroback01 is the OBS bucket name, we need create it in advance.
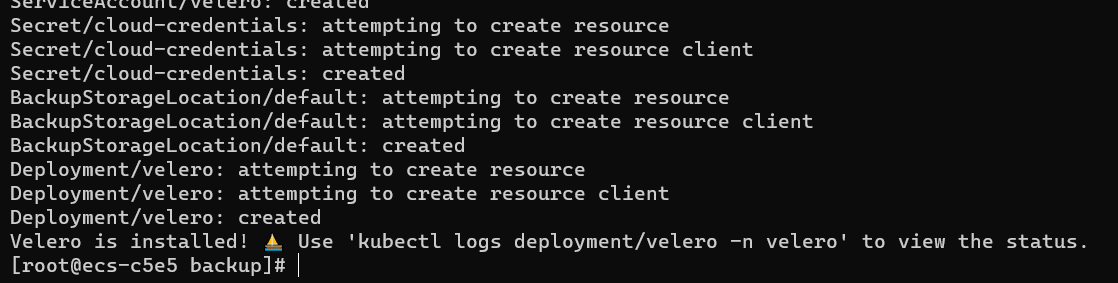
By default, a namespace named velero is created for the Velero instance. Run the following command to view the pod status:
| $ kubectl get pod -n velero
|
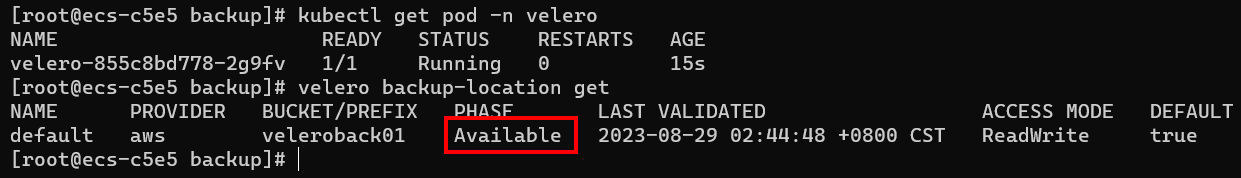
Check the interconnection between Velero and the object storage and ensure that the status is Available.
| $ velero backup-location get
|
2. create a application
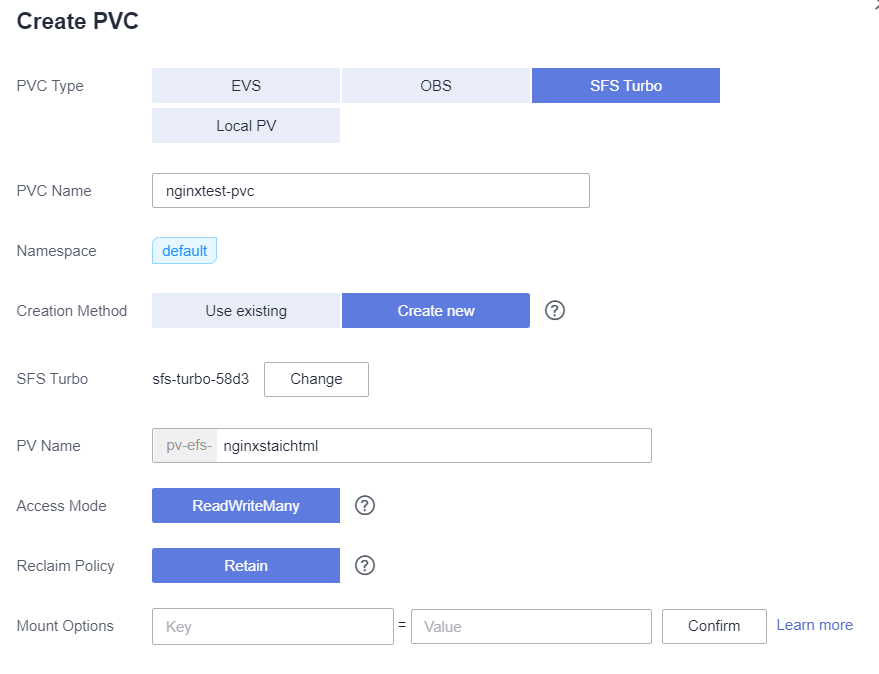
Create a nginx webapp and mount a SFS Turbo as the storage, the nginx access the page storage in SFS Turbo.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 | [root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# kubectl exec -it nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x -- /bin/bash
root@nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x:/# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
overlay 89G 2.5G 82G 3% /
tmpfs 64M 0 64M 0% /dev
tmpfs 7.6G 0 7.6G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
shm 64M 0 64M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/mapper/vgpaas-kubernetes 9.8G 63M 9.2G 1% /etc/hosts
/dev/mapper/vgpaas-dockersys 89G 2.5G 82G 3% /etc/hostname
192.168.34.245:/ 500G 0 500G 0% /usr/share/nginx/html
tmpfs 512M 12K 512M 1% /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
tmpfs 7.6G 0 7.6G 0% /proc/acpi
tmpfs 7.6G 0 7.6G 0% /proc/scsi
tmpfs 7.6G 0 7.6G 0% /sys/firmware
root@nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x:/# cd /usr/share/nginx/html/
root@nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x:/usr/share/nginx/html# ls
root@nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x:/usr/share/nginx/html# echo "111111" > index.html
root@nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x:/usr/share/nginx/html# echo "2222" > h1.html
root@nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x:/usr/share/nginx/html# exit
exit
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# curl 172.16.0.157
111111
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# curl 172.16.0.157/h1.html
2222
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x 1/1 Running 0 114s 172.16.0.157 192.168.34.204 <none> <none>
nginx-685fcffdbf-tk2sw 1/1 Running 0 114s 172.16.0.20 192.168.34.211 <none> <none>
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# curl 172.16.0.20
111111
|
Installing the Migration Tool
backup
Backup the nginx and delete the deployment, after this use the backup to restore.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47 | [root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# velero backup create backup20230828
Backup request "backup20230828" submitted successfully.
Run `velero backup describe backup20230828` or `velero backup logs backup20230828` for more details.
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# velero backup describe backup20230828
Name: backup20230828
Namespace: velero
Labels: velero.io/storage-location=default
Annotations: velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-gitversion=v1.25.3-r0-25.2.19
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-major-version=1
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-minor-version=25+
Phase: Completed
Namespaces:
Included: *
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: <none>
Cluster-scoped: auto
Label selector: <none>
Storage Location: default
Velero-Native Snapshot PVs: auto
TTL: 720h0m0s
CSISnapshotTimeout: 10m0s
ItemOperationTimeout: 1h0m0s
Hooks: <none>
Backup Format Version: 1.1.0
Started: 2023-08-29 03:21:14 +0800 CST
Completed: 2023-08-29 03:21:23 +0800 CST
Expiration: 2023-09-28 03:21:14 +0800 CST
Total items to be backed up: 607
Items backed up: 607
Velero-Native Snapshots: <none included>
|
restore
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51 | [root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# velero backup get
NAME STATUS ERRORS WARNINGS CREATED EXPIRES STORAGE LOCATION SELECTOR
backup20230828 Completed 0 0 2023-08-29 03:21:14 +0800 CST 29d default <none>
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# velero restore create --from-backup=backup20230828
Restore request "backup20230828-20230829032715" submitted successfully.
Run `velero restore describe backup20230828-20230829032715` or `velero restore logs backup20230828-20230829032715` for more details.
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# velero restore describe backup20230828-20230829032715
Name: backup20230828-20230829032715
Namespace: velero
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Phase: InProgress
Estimated total items to be restored: 511
Items restored so far: 87
Started: 2023-08-29 03:27:15 +0800 CST
Completed: <n/a>
Backup: backup20230828
Namespaces:
Included: all namespaces found in the backup
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: nodes, events, events.events.k8s.io, backups.velero.io, restores.velero.io, resticrepositories.velero.io, csinodes.storage.k8s.io, volumeattachments.storage.k8s.io, backuprepositories.velero.io
Cluster-scoped: auto
Namespace mappings: <none>
Label selector: <none>
Restore PVs: auto
Existing Resource Policy: <none>
ItemOperationTimeout: 1h0m0s
Preserve Service NodePorts: auto
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x 1/1 Running 0 8s
nginx-685fcffdbf-tk2sw 1/1 Running 0 7s
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-685fcffdbf-lrh2x 1/1 Running 0 12s 172.16.0.158 192.168.34.204 <none> <none>
nginx-685fcffdbf-tk2sw 1/1 Running 0 11s 172.16.0.21 192.168.34.211 <none> <none>
[root@ecs-c5e5 ~]# curl 172.16.0.158
111111
|
Note: If we need migrate the PV data, we can use the pv-migrate tool for sync the PV data.
Another Choice: CBR, rsync, OMS and etc.
3. Disaster Recovery
In a production environment, if you want to implement cross-region backup and recovery, you need to proceed as shown in the figure below.
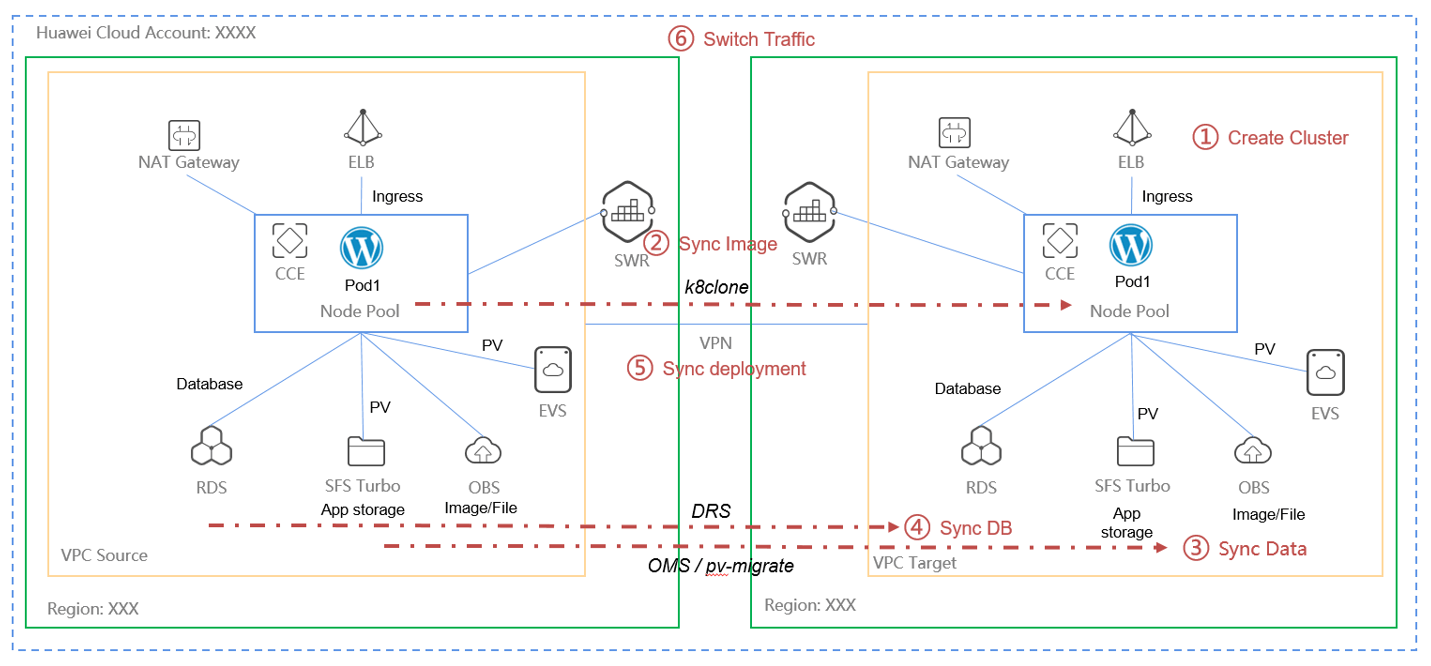
If runing in the same region, it's easy then this digram.
For application High Availability, we can also use the UCS service manage mulit-cluster running application.
Disaster Recovery: Implementing High Availability for Containers in CCE
捐赠本站(Donate)

如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))





